
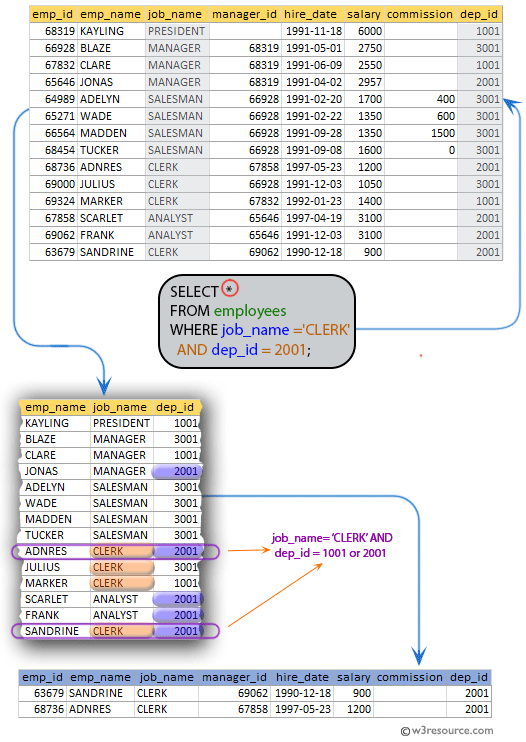
#Excel query table with variable sql how to#
The following code example shows how to create a QueryDef object with a simple SQL statement. In this section, you'll build the same statements as in the previous section, but this time using ADO as the data access method. Dim dbs As Database, qdf As QueryDef, strSQL As String
#Excel query table with variable sql full#
Be aware that you provide the full reference to the control, and that you include the number signs (#) that denote the date within the string. The following example creates a QueryDef object by using a value in a control called OrderDate on an Orders form.
StrSQL = "SELECT * FROM Orders WHERE OrderDate" _ Be aware that the number signs (#) that denote the date values must be included in the string so that they are concatenated with the date value. The next example creates the same QueryDef object by using a value stored in a variable. Set qdf = dbs.CreateQueryDef("SecondQuarter", strSQL) StrSQL = "SELECT * FROM Orders WHERE OrderDate >#3-31-2006# " This query returns all orders from an Orders table that were placed after March 31, 2006. The following example shows how to create a QueryDef object with a simple SQL statement. Therefore, you must construct your SQL statement so that Access first determines these values and then concatenates them into the SQL statement that is passed to the Access database engine.
The Access database engine processes all SQL statements, but not variables or controls. If this is the case, you need to include variables or control values in your query. Often a query must be based on values that the user supplies, or values that change in different situations. To construct an SQL statement, create a query in the query design grid, switch to SQL view, and copy and paste the corresponding SQL statement into your code. But if you are using an ADO Recordset object, you must set its Source property to a valid SQL string. This is sometimes referred to as taking your SQL code "inline."įor example, if you are creating a new QueryDef object, you must set its SQL property to a valid SQL string. When working with Data Access Objects (DAO) or ActiveX Data Objects (ADO), you may need to construct an SQL statement in code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
